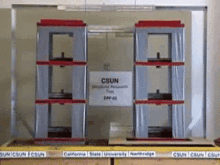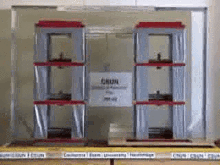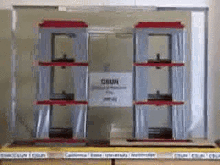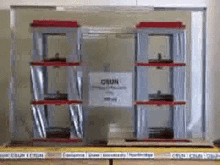
Base Isolation System is one of the common means of protecting structures against earthquake forces. This system is a collection of structural elements that must substantially separate a superstructure from its substructure that is resting on the shaking ground in order to protect a building or a non-building structure against earthquake.
It is one of the most powerful techniques of earthquake engineering and is related to the passive structural vibration control technologies. It is meant to protect a building or non-building structure against seismic impact through a proper initial design or subsequent modifications.
In some cases, application of base isolation can significantly improve both a structure's seismic performance and its seismic sustainability. Contrary to popular belief, base isolation does not make a building earthquake-proof. It should be noted that this technology can be employed both while designing a new project and later for its seismic retrofit.
As mentioned, this technology can be used for both new structure designs and seismic retrofit. Some of the most prominent U.S. monuments such as Pasadena City Hall, San Francisco City Hall, Salt Lake City and LA City Hall have gone through the process of seismic retrofit using this system. It required creating rigidity diaphragms and moats around the buildings to make them equipped against overturning and P-Delta Effect.


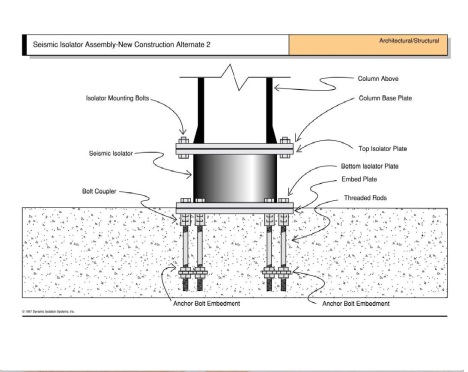
The concept of base isolation is quite simple. The seismic isolator is usually installed between the structure and the foundation (or in the case of bridges between the deck and the base) and because it has relatively low horizontal stiffness, it Increases the degree of freedom of the structure in the horizontal direction. This significantly reduces the natural frequency of the structure compared to its fixed-base frequency, keeping it away from resonance, which occurs at high frequencies. The first dynamic mode of the isolated structure involves horizontal deformation only in the seismic isolation system and the upper-structure almost rigidly moves.
Higher modes that will produce deformation in the structure are orthogonal to the first mode and also to the ground motion. These higher modes do not participate in the motion, therefore the possible high seismic energy, won't be transmitted into the structure.
In fact, the purpose of the isolation system is not to absorb the earthquake energy (unlike dampers or plastic joints), but rather to alter the dynamic modes of the system and deflect the energy.
And so, the most important outcome of seismic isolation, is expansion of time period of structures from a 0.1 - 1 second period (in which applying high accelerations to the system is possible), to 2 - 3 seconds.
In addition, there is a mechanism that increases damping in seismic isolator and causes higher energy absorption. Seismic isolation equipment tolerate the increased drift demand caused by time period transition, and this allows the upper-structure to move as a rigid object.
Using Seismic Base Isolators in Structure Design and Retrofit
Base isolation system consists of isolation units and isolation components:
-Isolation units are the fundamental elements of a base isolation system which are responsible for bringing the mentioned separation effect to a building or non-building structure.
-Isolation components are the connections between isolation units and the parts that have no separation effect of their own.
All isolation units, based on their response to earthquake, could be categorized into either shear units or sliding units.
Some of the earliest uses of base isolation system date back all the way to the 6th century B.C. in the construction of the Tomb of Cyrus the Great in the ancient city of Pasargadae, Iran. This system was composed of two foundation layers, one layer made of a deep, wide stone and smoothed mortar, underneath another layer made of flat and polished stones. The two foundations were connected in such a way that they could slide back and forth in case of an earthquake. And as a result, the Tomb of Cyrus the Great still stands today.